Basail Pourashava Master Plan
Strategic Urban Plan 2024-2044
The Planning Vision
Vision 2044
To establish Basail Pourashava as a liveable, safe, clean, inclusive, eco-friendly, sustainable, and tourism-friendly city that provides equal opportunities for all citizens and improves quality of life.
The plan adopts a decentralized approach, ensuring basic civic amenities reach every ward while protecting the region's agricultural and aquatic heritage.
Strategic Planning Framework
The master plan utilizes a hierarchical structure combining a 20-year Strategic Plan, a 10-year Urban Area Plan, and a 5-year Ward Action Plan.
Land Use Strategy
- Core Urban Area: High-density development, vertical expansion.
- Peripheral Area: Controlled extension, protecting green zones.
- Agricultural Zone: Conservation of primary farming land (59.46% of total area).
- Water Bodies: Strict protection of rivers (Langulia, Bangshi) and canals.
Transport & Connectivity
- Road Hierarchy: Primary (80ft), Secondary (45-80ft), and Tertiary networks.
- Pedestrian First: Focus on "Walking City" concepts with sidewalks and safety.
- Water Transport: Revitalizing canals for transport and tourism.
- Infrastructure: New bus terminals and auto-rickshaw stands.
Housing & Settlement
- Affordable Housing: Focus on low-income groups and diverse housing.
- Compact Design: Encouraging vertical growth over horizontal sprawl.
- Resilience: Raising plinth levels for flood protection.
- Block Development: Planned Unit Development (PUD) incentives.
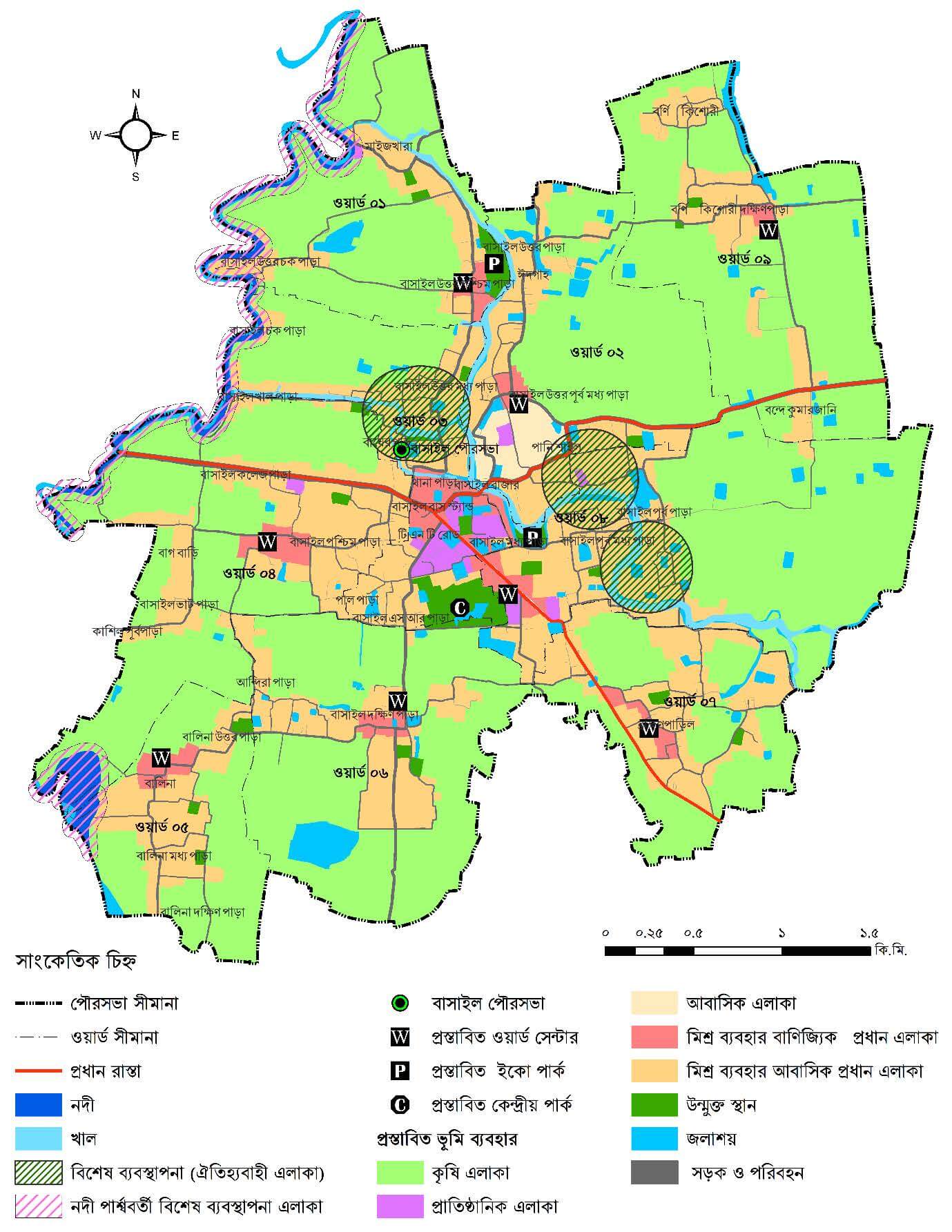
Proposed Land Use Distribution
The plan prioritizes agriculture while accommodating urban growth through strategic zoning.
Key Planning Maps & Models
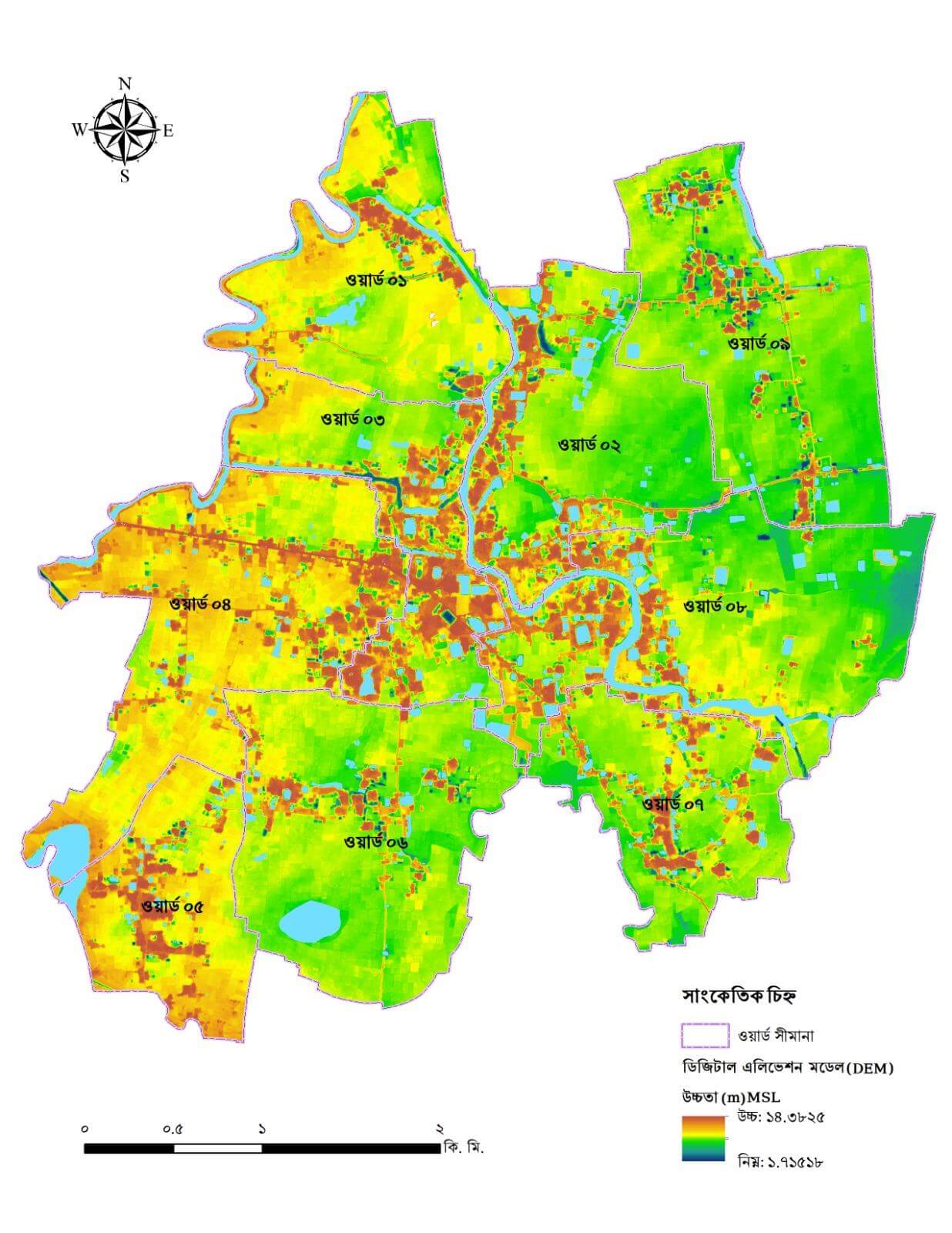
Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
Visualizes the elevation profile of Basail, critical for analyzing slope, determining drainage patterns, and identifying low-lying areas prone to waterlogging.
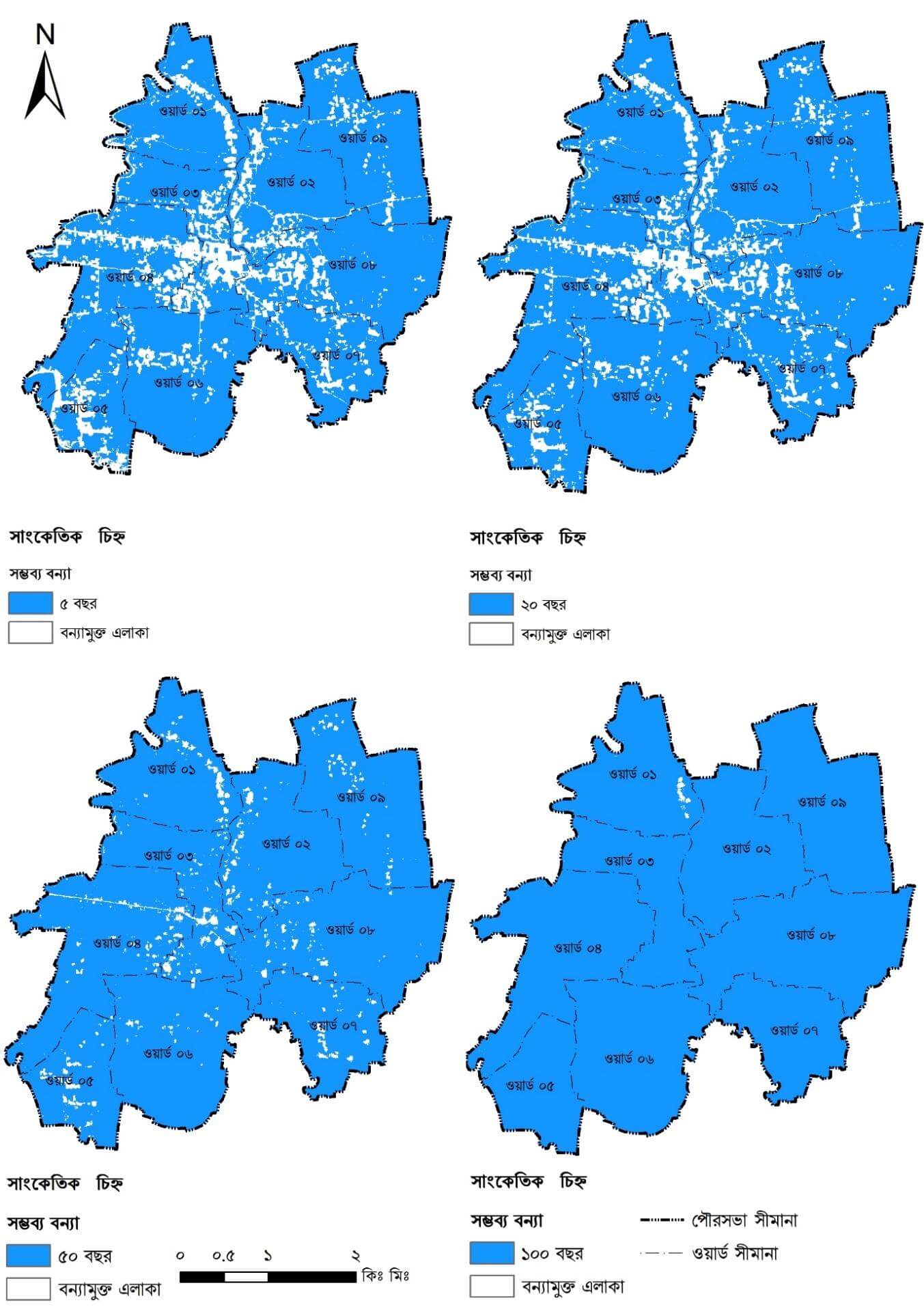
Flood Zone Map
Identifies high-risk areas susceptible to flooding from the Langulia and Bangshi rivers, guiding resilient construction standards and land use planning.
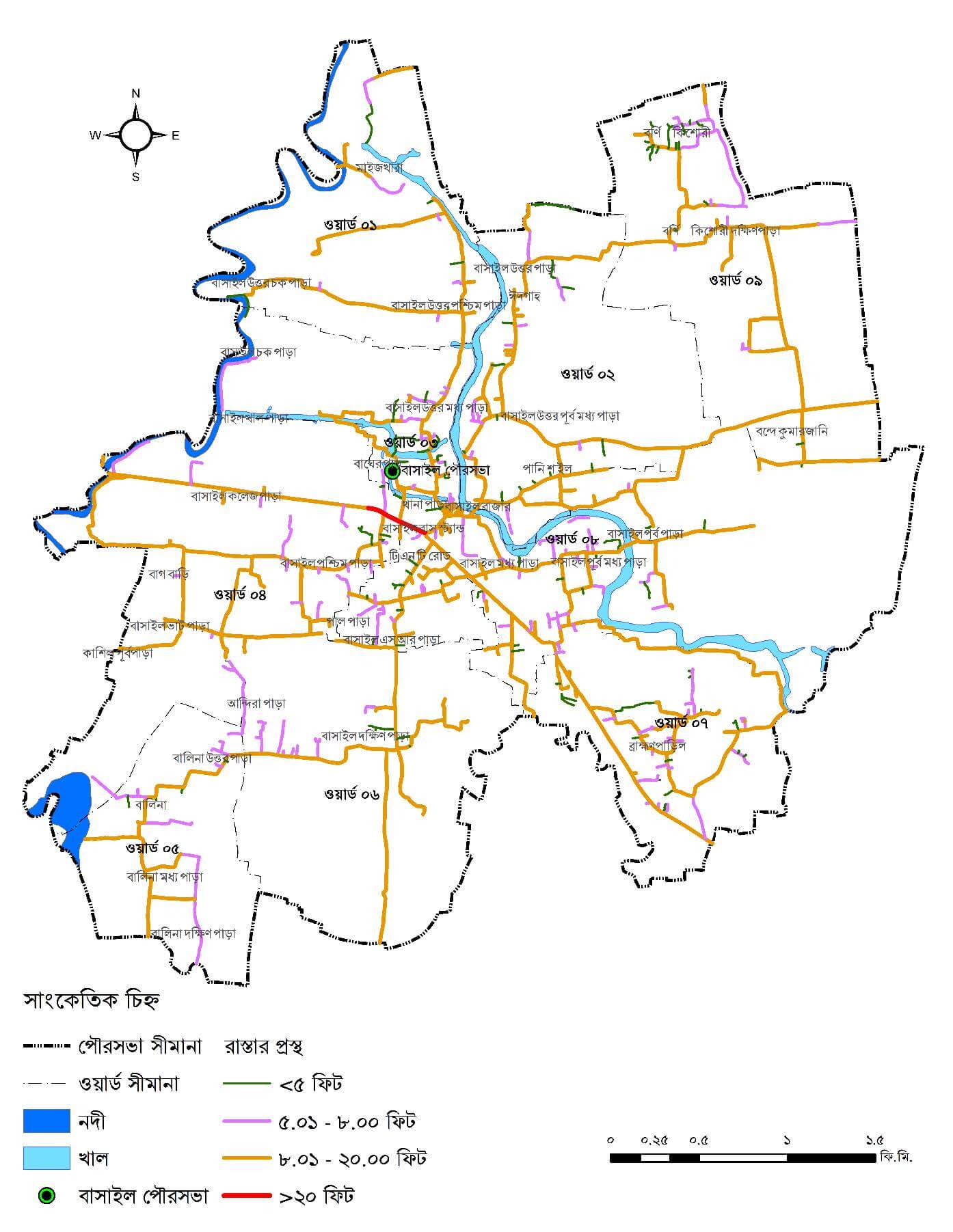
Transportation Network
Detailed layout of the road hierarchy (Primary, Secondary, Tertiary), proposed widening projects, bridge locations, and connectivity hubs.
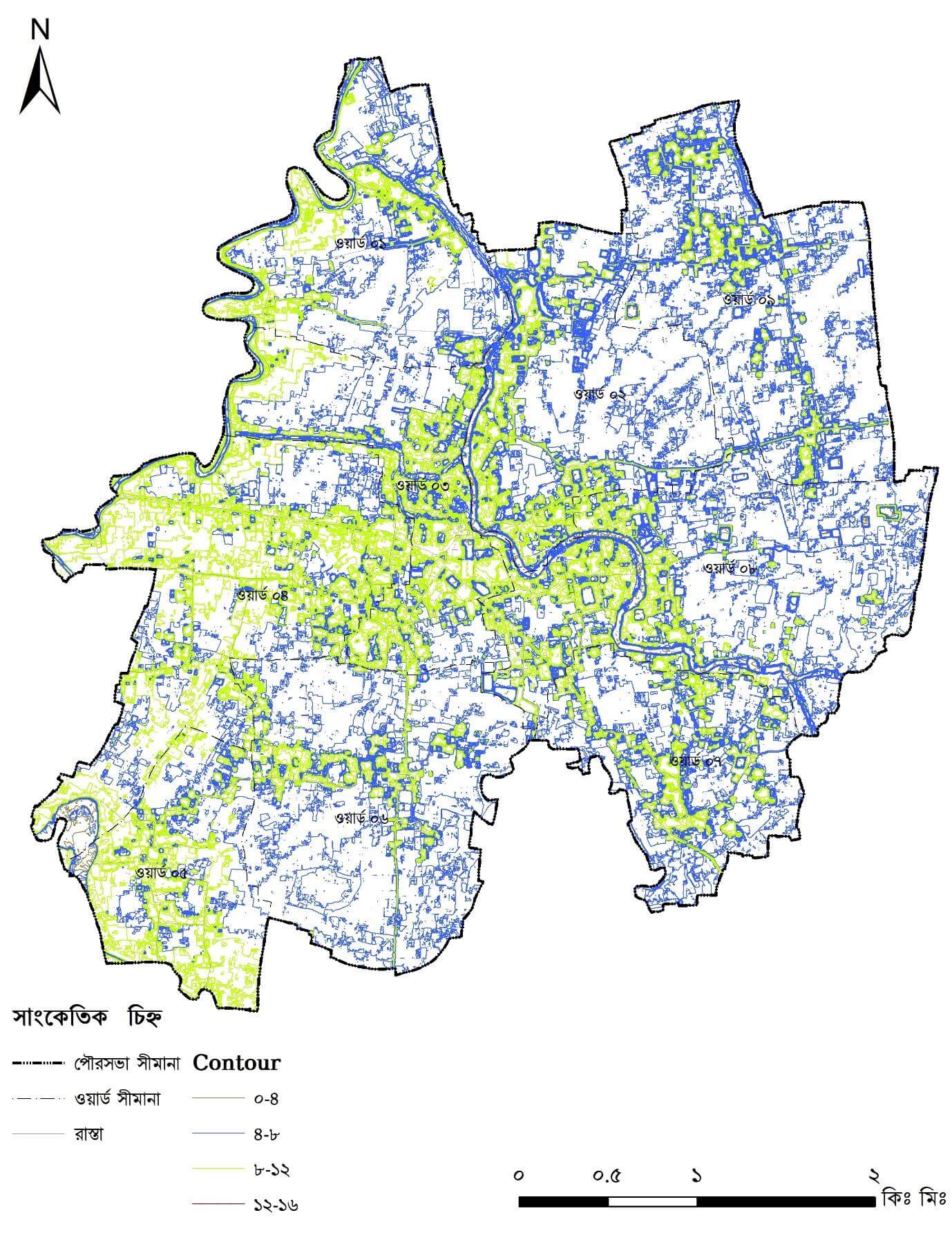
Contour Map
Topographic lines at 0.5m intervals representing the terrain's shape, essential for designing effective drainage systems and calculating earthwork.
Disaster Management & Resilience
Flood Management
Raising plinth levels for new constructions (Base Flood Level + Safety Factor) and preserving natural drainage channels like the Langulia River.
Lightning Protection
Installation of lightning sheds in open agricultural areas (Haors/Beels) to protect farmers and fishermen during storms.
Blue-Green Infrastructure
Utilizing bioswales, retention ponds, and rainwater harvesting to manage stormwater run-off sustainably and reduce waterlogging.
Implementation Timeline
Phase 1 (Years 1-5)
Priority infrastructure: Road widening, Ward Centers, Kitchen Markets, and initial Drainage improvements.
Phase 2 (Years 6-15)
Major expansion: Housing projects, Eco-parks, Water treatment plants, and secondary road networks.
Phase 3 (Years 16-20)
Consolidation: Completion of the tourism network, full coverage of utility services, and long-term maintenance strategies.
Urban Planning Tools & Techniques Learned
A master plan project of this scale utilizes diverse methodologies for data collection, analysis, and strategy formulation.
Qualitative research technique used to gather in-depth insights from specific community groups (farmers, youth, women) regarding local problems and needs.
One-on-one interviews with community leaders, officials, and experts to get specialized knowledge and strategic viewpoints on urban issues.
An approach enabling local people to share, enhance, and analyze their knowledge of life and conditions, ensuring community-led planning.
Geographic Information Systems used for land use mapping, spatial analysis, and creating the database for all physical features.
Strategic framework used to identify the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to various sectors like housing, transport, and economy.
A set of theories and techniques for analyzing spatial configurations, particularly useful for understanding road network connectivity and integration.
Use of software like HEC-RAS or SWMM to simulate flood scenarios and drainage capacity, crucial for disaster-resilient planning.
Statistical techniques (e.g., compound growth rate) to estimate future population size, essential for calculating future demand for services and land.