Smart Aquaculture
City Blueprint
A comprehensive master plan to transform 8,080 acres in Cox's Bazar into a sustainable, climate-resilient, and economically vibrant shrimp estate supporting the Blue Economy.
Project Impact Targets
Context
Located in Chakaria Upazila. Currently 8,080 acres of mostly extensive farming with dilapidated infrastructure.
Challenge
Low productivity (50-500 kg/ha), poor water management, and high mortality rates due to lack of technology.
Ecology
Former "Chakaria Sundarbans" area. Restoration of mangrove buffers is critical for climate resilience.
Phased Development Scenarios
A staged approach to modernize infrastructure, expand capacity, and integrate technology.
Scenario 1
Restructuring & Foundation
- Re-excavation of all leased plots.
- Improved-Extensive (Dominant) + Limited Semi-Intensive pilot.
- CSPPZ Phase 1 (85 acres) establishment.
- Construction of Badarkhali Bridge & 26 sluice gates.
Est. Production
~5,978 MT
Scenario 2
Expansion & Institutions
- Expansion to 29,456 acres (surrounding areas).
- Widespread transition to Semi-Intensive farming.
- Blue Economy Research Institute established.
- CSPPZ expansion to 130 acres.
Est. Production
~28,915 MT
Scenario 3
Integrated Smart Estate
- Pilot Intensive Aquaculture (471 acres).
- 113km Peripheral Dyke for total flood defense.
- Renewable Energy Corridor (Solar/Wind).
- Full CSPPZ (188 acres) & Eco-Tourism.
Est. Production
~48,428 MT
Analytics & Master Plan Maps
Data-driven projections and spatial layouts.
Production Targets (Metric Tons)
Source: Tables 3-1, 3-4, 3-6 (Implementation Report)
Scenario 3 Land Use (Acres)
Master Plan Visualizations
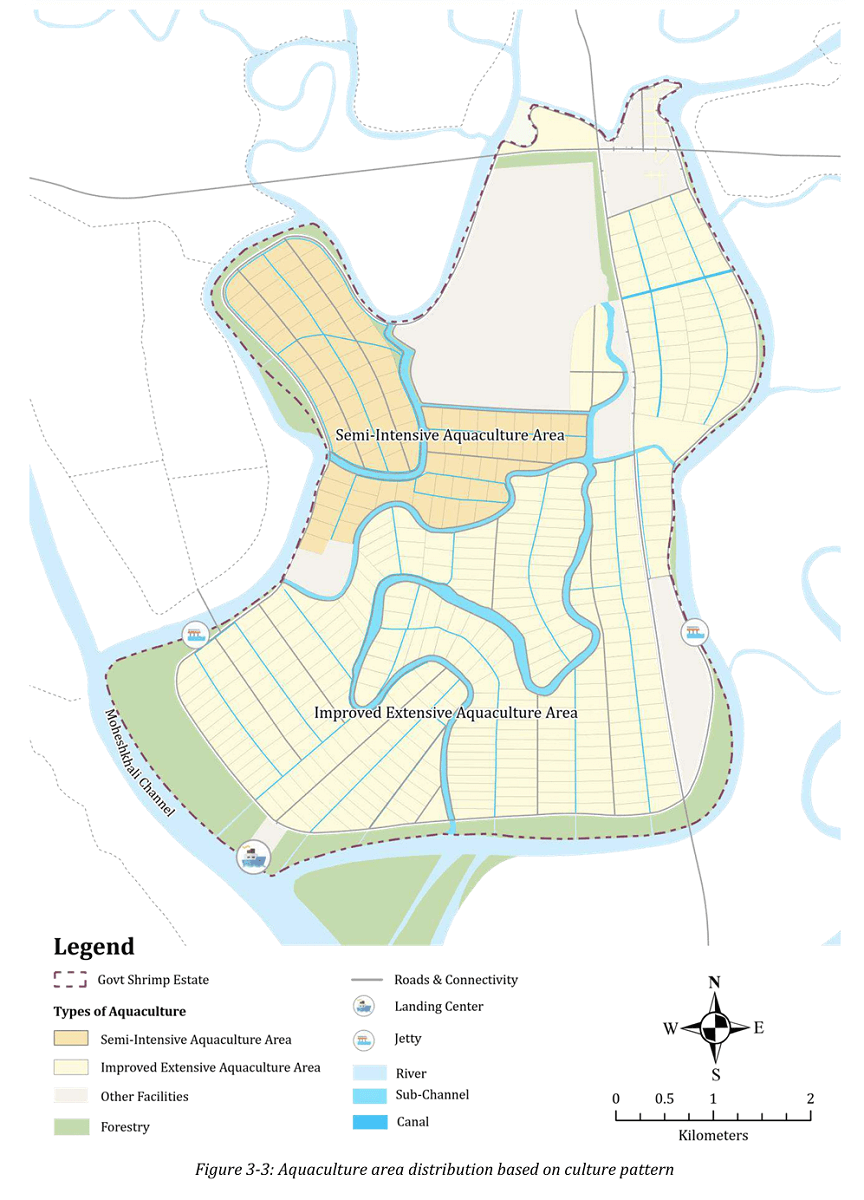
Scenario 1
Basic Layout & Restructuring
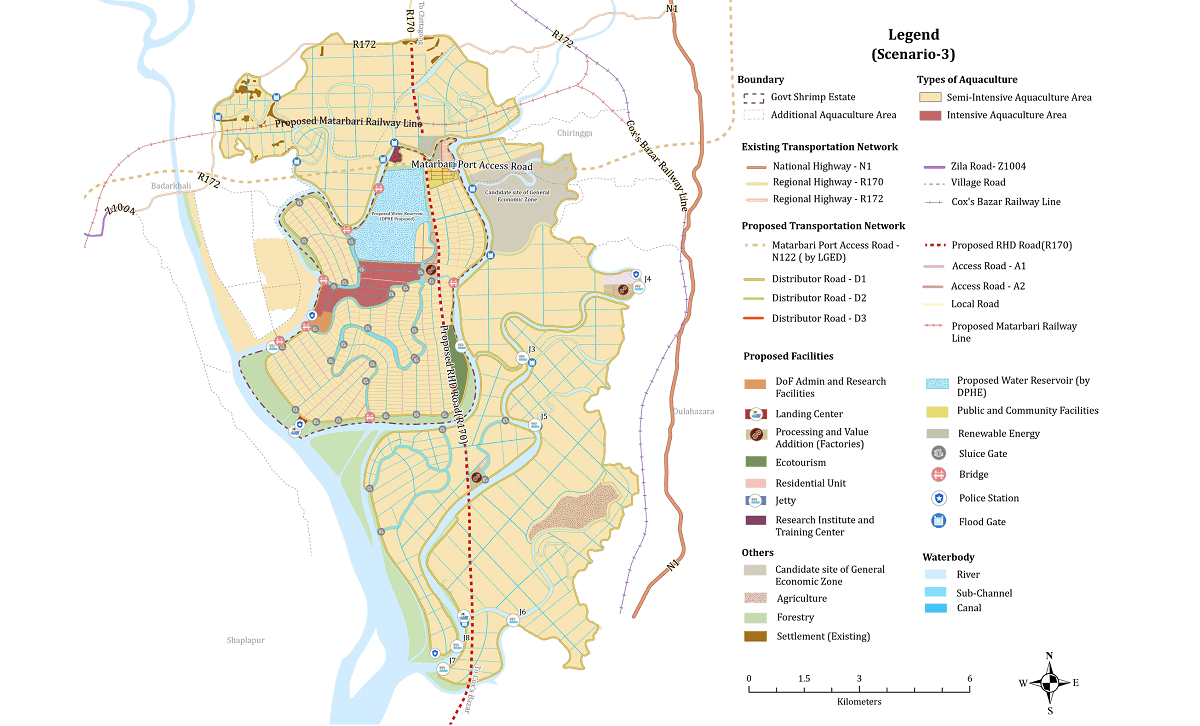
Scenario 3
Full Integration & Intensive Zones
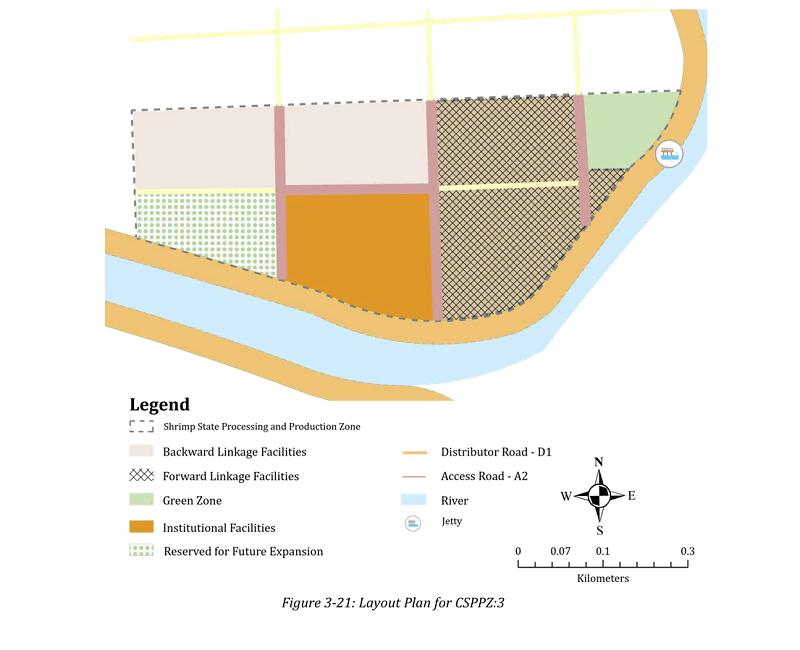
CSPPZ
Processing Zone Layout
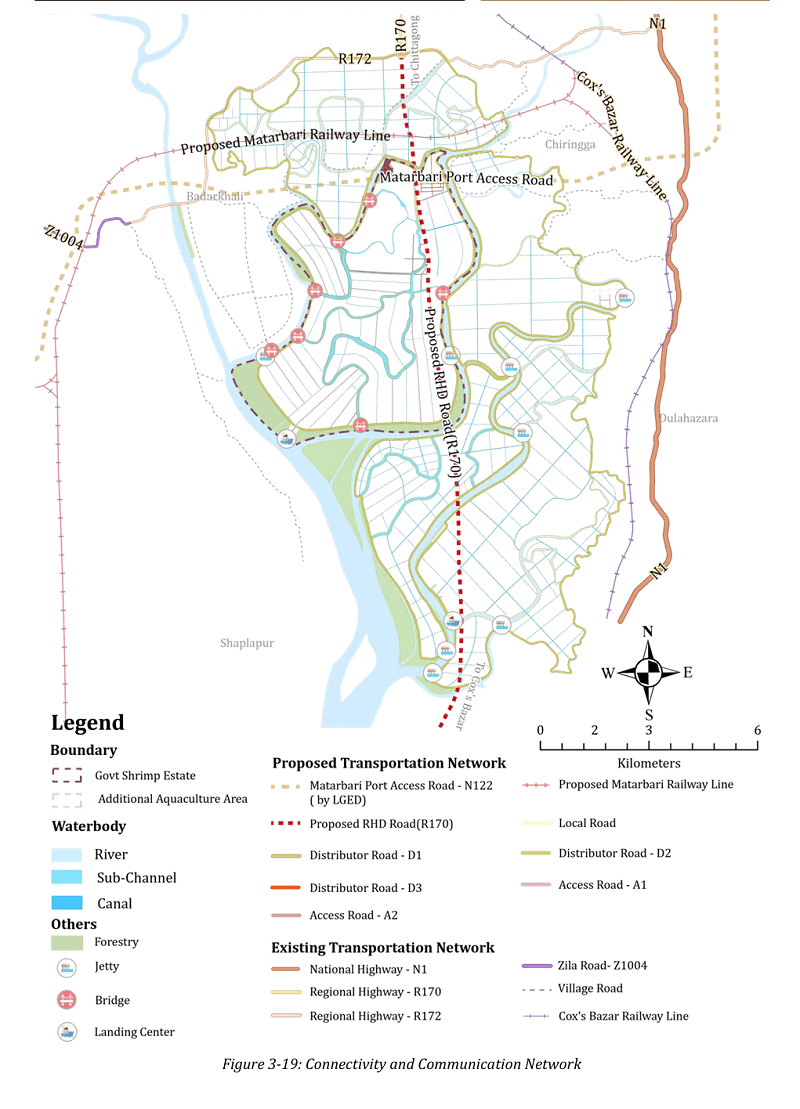
Infrastructure
Roads & Canal Network
Integrated Value Chain Model
From Hatchery to Export Market (Based on Figure 3-25)
Farming
Semi-Intensive & Intensive Ponds
Landing Centers
Sorting & Icing
CSPPZ
Processing & Value Addition
Sustainability & Society
Balancing economic goals with ecological health.
Green Belt Strategy
Extensive mangrove restoration (434 hectares) and dyke plantations to act as carbon sinks and storm buffers.
Renewable Energy
Dedicated 34-acre zone for Solar PV and Wind farms. Hybrid electrification for hatcheries and cold chains.
Eco-Tourism
188-acre zone along Bura Matarbari River featuring kayaking, promenades, and aquaculture museums.
Key Infrastructure Stats
Peripheral Dyke
113 km
Engineered to +6.67m MSL
Sluice Gates
32 Units
+11 Flood Gates
Jetties
8 Units
Multimodal Access
Security
5 Posts
Police Checkpoints
Key Planning Expertise & Strategic Insights
Learnings and methodologies derived from the master planning process.
Strategic Zoning & Land Use
Mastery in spatially segregating production (intensive/extensive), industrial processing (CSPPZ), and residential zones to minimize conflict and maximize efficiency.
Hydraulic Engineering
Designing hierarchical water control systems (main/sub canals, sluice/flood gates) tailored for salinity management and flood resilience.
Industrial Ecology (CSPPZ)
Planning integrated value chains where waste from one process (e.g., shrimp shells) becomes input for another (e.g., feed/chitosan), creating a circular economy.
Climate Adaptation Planning
Integrating hard infrastructure (dykes) with nature-based solutions (mangrove bio-shields) to protect assets against cyclonic surges.
Institutional Framework Design
Developing governance models that link research institutes with local farmers to ensure technology transfer and capacity building.
Phased Implementation Strategy
Skill in creating scalable roadmaps (Short/Mid/Long Term) that allow for gradual investment and infrastructure maturity.