PROJECT SNAPSHOT & EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Total Approved Budget
BDT 1020 Cr
(All GOB Grant Secured)
Implementation Window
5 Years
Feb 2020 – Jan 2025
Total Network Output
21.60 KM
Strategic Road & Pedestrian Paths
Connectivity Assets
140 Meters
New Bridges/Culverts
MANDATE & CORE OBJECTIVES:
- MASTERING DECONGESTION: Successfully widen and expand key road corridors to eliminate bottleneck traffic, specifically targeting high-pressureN8 Expressway intersections.
- CLIMATE RESILIENCE: Implement robust, modern surface drainage and utility systems to permanently combat chronic waterlogging and safeguard asset longevity.
- PRIORITIZING SAFETY:Construct 21.60 km of functional footpath and dedicated bicycle lane to ensure safe, accessible mobility for residents and promote Non-Motorized Transport (NMT).
- ECONOMIC CATALYSIS: Directly integrate the road network with future economic engines, including the International Sports Complex, Inter-District Terminals, and Major Residential Hubs
FINANCIAL ARCHITECTURE: STRATEGIC COST ALLOCATION
Core Investment Distribution (BDT 1,020 Cr Total)
Execution Timeline & Capital Flow (BDT in Lakh)
FY 2019-2020 (Launch Phase)
BDT 19,213.46 Lakh
FY 2020-2021 (Peak Mobilization)
BDT 33,872.69 Lakh
FY 2024-2025 (Finalization)
BDT 11,944.48 Lakh
ARCHITECTING SUCCESS: KEY STRATEGIC PLANNING ACHIEVEMENTS
My role ensured the project's strategic alignment, institutional compliance, and effective resource management, paving the way for successful implementation.
ECNEC Gateway & Budget Compliance
Successfully navigated the Planning Commission(PC)andProject Steering Committee (PSC)stages, securing the crucial MTBF (Medium-Term Budget Framework) certification. This meticulous preparation was fundamental to the project's eventual ECNEC approval, guaranteeing BDT 1020 Crore of GOB financing within the national framework.
Mastering Multi-Stakeholder Liaison
Established and maintained effective collaboration across critical entities. This involved coordinating LGED's plan with RHD (Roads and Highways Department)regarding the N8 Expressway intersections, ensuring the commitment of the Local Government Division, and gaining necessary consensus from localUnion Parishads and influential private sector housing developers.
Planned & Ethical Land Acquisition
Developed a robust land acquisition strategy for the 51.53 acresrequired for road expansion. By committing over 44% of the budget(~BDT 456.9 Cr) for compensation and adhering strictly toGovernment-determined land rates and acquisition rules ,we ensured rapid Right-of-Way (ROW) clearance while minimizing local disputes and displacement risks.
THE LIFEBLOOD OF KERANIGANJ'S FUTURE: 21.60 KM NETWORK
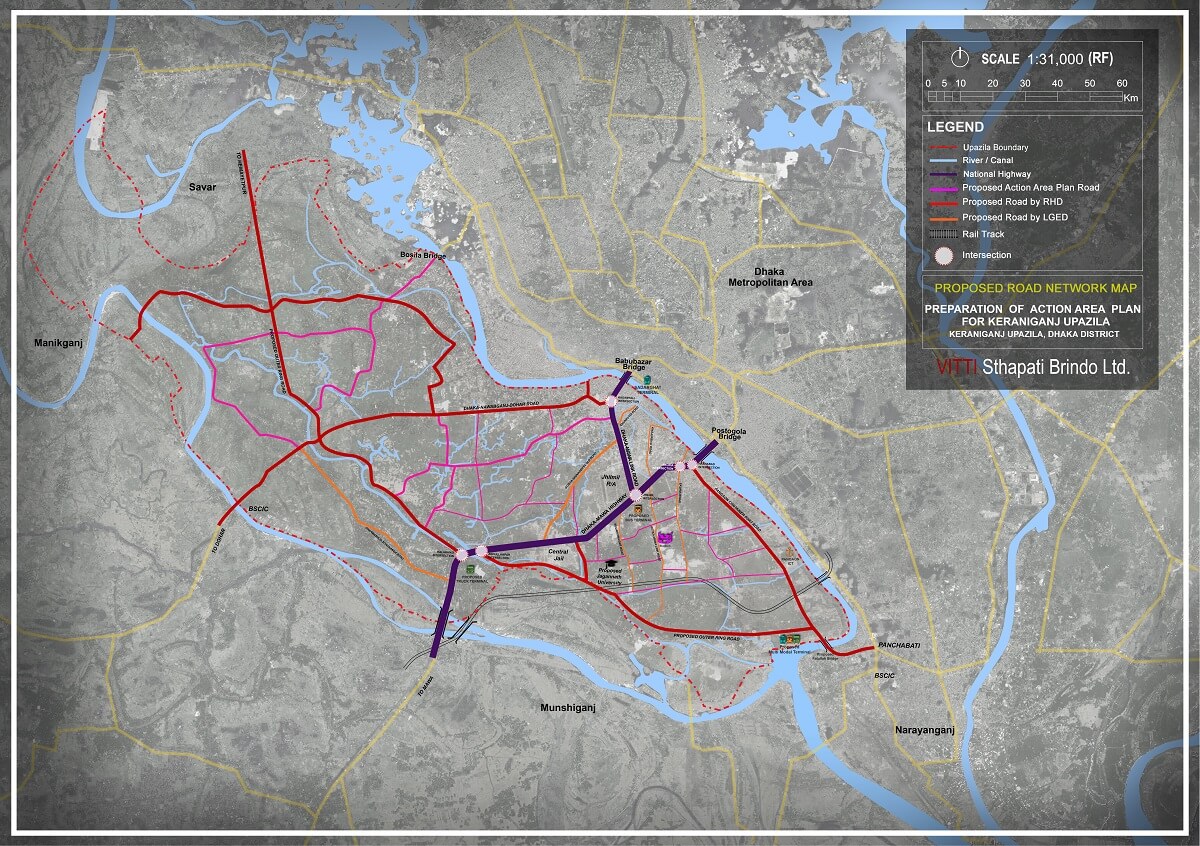
Strategic Schemes & Key Roles
| Road Name | Length (km) | Width (ft) |
|---|---|---|
| Ruhitpur GC-Baluartack | 6.03 | **80 ft** |
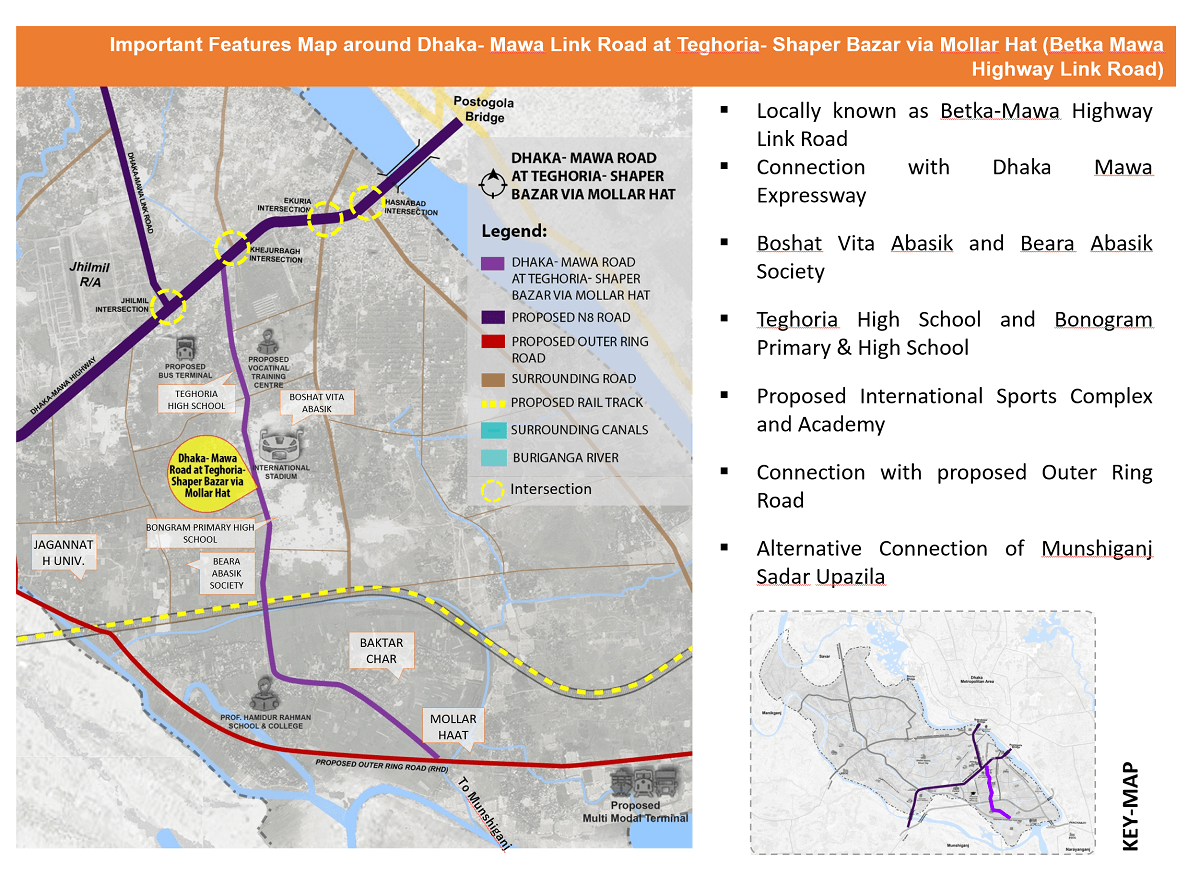
| Dhaka-Mawa Rd at Teghoria | 5.50 | **80 ft** |
| Zinzira-Konda (Ekuria Rd) | 4.065 | 50 ft |
| Chunkutia Auditorium | 4.00 | 46 ft |
| Dhaka Mawa-Khejurbagh | 2.00 | 25-35 ft |
The Strategic Imperative:
- Regional Bypass:The 80ft roads (Ruhitpur and Teghoria) create alternative high-capacity links, connecting Dhaka-Nawabganjand Dhaka-Munshiganjtraffic directly to the N8/Outer Ring Road corridor, bypassing Dhaka's core.
- Economic Corridors:Ruhitpur directly serves the Proposed Inter-District Truck Terminal, and Teghoria supports the futureMulti-Modal Terminal, positioning these roads as vital commercial arteries.
ENGINEERING EXCELLENCE: SUSTAINABLE URBAN DESIGN
The design sets a national precedent by integrating utility, drainage, and mobility solutions into a single, resilient structure. We are building assets, not liabilities.
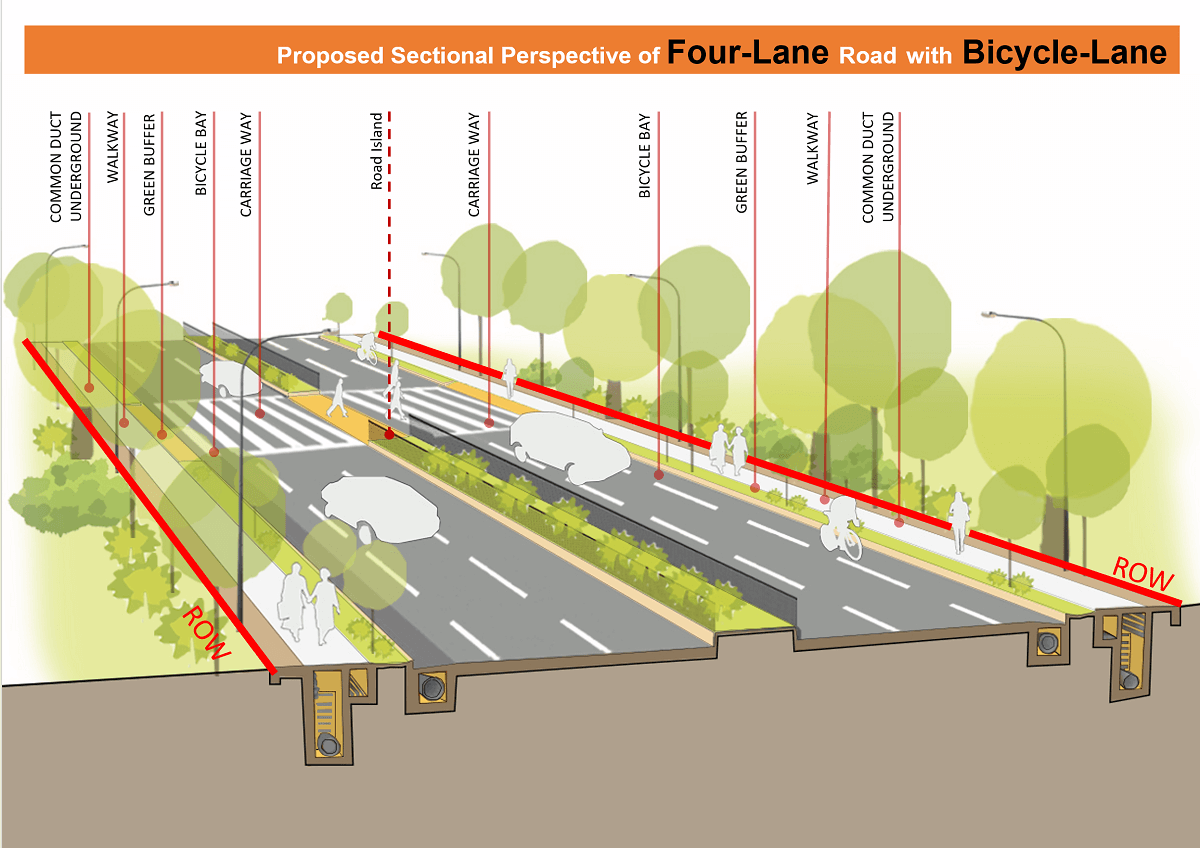
FIGURE: 80 FT CROSS-SECTION (4-LANE & NMT INTEGRATION)
- ✓ 4-Lane Carriageway (3m wide lanes)
- ✓ Dedicated Bicycle Lanes (1.8m)
- ✓ Functional Footpaths (2m)
DETAIL: REVOLUTIONARY COMMON UTILITY DUCT (CUD)
The CUD eliminates wasteful road-cutting by utility agencies, radically lowering maintenance costs and guaranteeing the road's lifespan and smooth traffic flow.
INSTITUTIONAL GOVERNANCE & LONG-TERM ASSET SUSTAINABILITY
Strategic Project Oversight
The project's success is ensured by rigorous multi-level oversight, linking strategic policy to field execution:
- Project Steering Committee (PSC):Provides crucialhigh-level policy directionand conflict resolution (Chaired by Division Secretary).
- Project Implementation Committee (PIC):Drives operational efficiency and technical compliance on the ground (Chaired by Chief Engineer, LGED).
Sustainable Investment Protection
We planned for perpetual asset value through climate-resilient design and dedicated funding mechanisms:
- Perpetual O&M Mandate: Maintenance is secured under the Rural Road and Bridge/Culvert Policy - 2013, integrated into the LGED revenue budget.
- Financial Assurance: Proactive maintenance budgeting allocates BDT 2.00 Lakh/km/year for roads, protecting the massive capital investment against degradation.
IMPACT & THE NATIONAL AGENDA (SDGS)
Profound Socio-Economic Transformation
- Reduced Costs Farmers and businesses benefit from dramatically lower transport time and costs, directly increasing profitability.
Poverty Alleviation Direct job creation during construction (including targeted employment for women) and long-term economic acceleration drive rural poverty reduction.- Human Capital:Improved road access ensures faster response times for health services, helping reduce maternal and infant mortality rates.
ALIGNMENT WITH NATIONAL VISION
SDG 1 (No Poverty): A direct tool for economic empowerment and poverty eradication.
SDG 5 (Gender Equality): Enhances women's mobility and access to opportunities, fostering empowerment.
SDG 9 (Infrastructure): Achieves the core mandate of building resilient, high-quality, and inclusive public infrastructure.